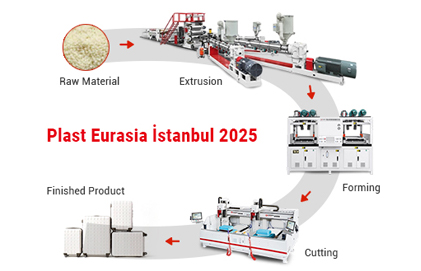
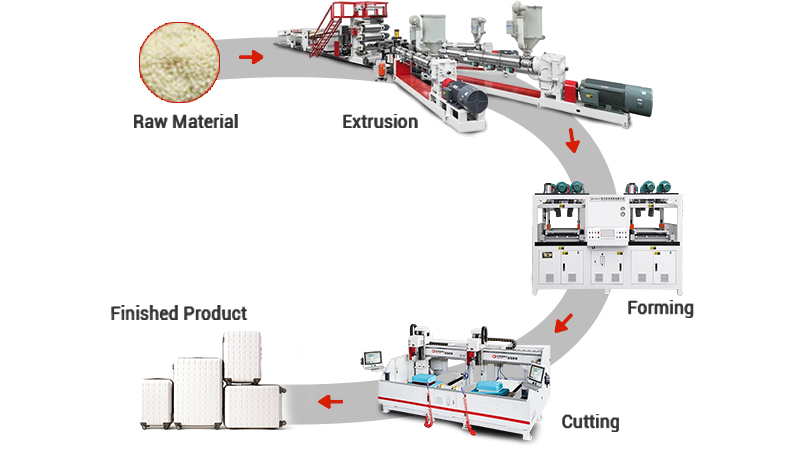
Have you ever wondered how that clear, sturdy clamshell packaging for your electronics is made? Or the durable plastic lid on your coffee cup? The journey of these everyday items often begins with two powerful manufacturing processes: plastic sheet extrusion and thermoforming. Together, they transform raw plastic into the familiar shapes we use daily.
This article breaks down these processes in a simple, structured way.
Part 1: The Foundation - Plastic Sheet Extrusion
Think of extrusion as the "birth" of the plastic sheet. It's the process of creating a continuous, flat sheet of plastic of a specific thickness and consistency. This sheet is the essential raw material for the next step.
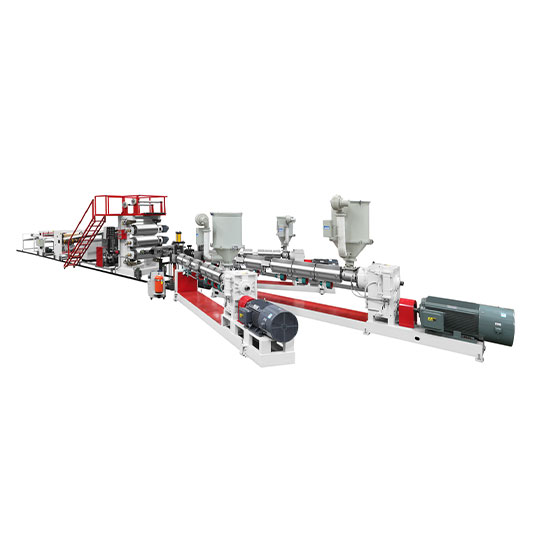
The heart of this operation is the Plastic Sheet Extruder Machine.
How Does a Plastic Sheet Extruder Machine Work?
A plastic sheet extruder line is not a single machine but a coordinated system. Here’s a step-by-step look at how it works:
1. Feeding: The process starts with raw plastic material, usually in the form of small pellets or granules. These pellets are fed from a large hopper into the barrel of the extruder.
2. Melting and Mixing: Inside the barrel, a large, rotating screw is housed. As the screw turns, it pushes the plastic pellets forward. The barrel is heated by external heaters, and the friction from the screw itself generates additional heat. This combination of heat and pressure melts the plastic into a thick, viscous liquid. The screw also ensures the melt is thoroughly mixed and uniform in temperature.
3. Filtering and Forming: The molten plastic is then forced through a filter screen to remove any contaminants. It next flows into a critical component called the " die." For sheet extrusion, a flat, wide die (like a wide, horizontal slit) gives the plastic its sheet-like shape as it exits.
4. Cooling and Sizing: The hot, soft plastic sheet then enters a set of precision-calibrated cooling rolls (calender rolls). These chilled metal rolls press the sheet to the exact desired thickness, smooth its surface, and cool it down until it solidifies.
5. Pulling and Winding: Finally, pull rolls gently to draw the now-solid sheet away from the cooling rolls. The continuous sheet is either wound into a large roll for storage and shipment or cut into specific lengths for immediate use.
The result is a uniform, high-quality plastic sheet ready to be transformed.
Part 2: The Transformation - Thermoforming
If extrusion creates the canvas, then thermoforming is the act of painting the masterpiece. Thermoforming is the process of heating an extruded plastic sheet until it becomes soft and pliable, then forming it into a specific three-dimensional shape using a mold.
How Does Thermoforming Work?
The process is surprisingly straightforward:
1. Clamping: A section of the extruded plastic sheet is securely clamped into a frame.
2. Heating: The sheet is then heated using radiant heaters until it becomes soft and stretchable—like a piece of warm taffy. The heating must be even to ensure consistent forming.
3. Forming: The soft sheet is then shaped. There are two primary methods:
Vacuum Forming: A mold is pressed close to the sheet, and a powerful vacuum sucks all the air out from between the sheet and the mold. Atmospheric pressure then pushes the soft plastic tightly onto the mold, copying its shape perfectly.
Pressure Forming: Compressed air is blown onto the side of the sheet opposite the mold, forcefully pushing it into the mold's details. This method allows for sharper details and more complex shapes.
4. Cooling and Trimming: The plastic is allowed to cool and harden in the mold. Once solid, the formed part is removed from the machine. The final step is to trim away the excess plastic from around the shaped product, leaving a clean, finished item.
The Perfect Partnership
It's clear that extrusion and thermoforming are a perfect industrial partnership. You cannot have one without the other in this context.
The Plastic Sheet Extruder Machine creates the uniform, consistent, and high-quality raw material.
Thermoforming efficiently and cost-effectively transforms that material into a nearly infinite variety of useful products.
This combination is why these processes are so popular for manufacturing items like:
In conclusion, from the raw pellet to the final product, the journey of a plastic item is a fascinating dance of heat, pressure, and precision engineering. The plastic sheet extrusion process.